
Metal Forming Methods – Altron’s
Metal forming is a fundamental process in manufacturing. It transforms metal sheets into desired shapes and configurations. At Altron, we employ various metal-forming techniques to meet diverse industry needs. This blog delves into our primary metal-forming methods, explaining each in detail.
Altron provides OEM and ODM customized services in the field of sheet metal forming! Spinning, deep drawing, stamping, etc.!

Metal Spinning
Introduction to Metal Spinning
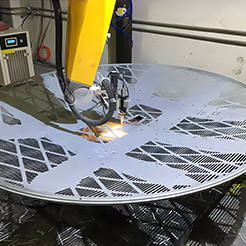
Metal spinning, also known as spin forming, involves rotating a metal disc while applying force to shape it. This method creates symmetrical objects such as cones, cylinders, and hemispheres.
Process Overview
The metal disc is clamped onto a lathe. As it spins, a roller or stylus shapes the metal. The force applied must be consistent to avoid defects. This technique is ideal for small to medium production runs.
Applications
Metal spinning is used in producing satellite dishes, musical instruments, and kitchenware. It’s valued for its precision and cost-effectiveness.
Flanging
What is Flanging?
Flanging forms flanges or rims on the edge of a metal piece. This technique adds strength and facilitates assembly with other parts.
Flanging Techniques
There are several flanging methods, including mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic. Each method uses different force applications to achieve the desired flange.
Uses and Benefits
Flanging is common in automotive and aerospace industries, where strong, precise joints are crucial. It enhances structural integrity and ease of assembly.
Deep Drawing
Deep Drawing Basics
Deep drawing involves pulling a metal blank into a die to form a deep, hollow shape. This process can create complex, high-strength components.
Process Steps
A blank holder clamps the metal sheet. A punch then pushes the sheet into the die cavity, forming the part. Deep drawing requires precise control of material flow and pressure.
Applications
This method is used in manufacturing automotive parts, appliance housings, and beverage cans. It allows for high-volume production of uniform parts.
Stamping
Introduction to Stamping
Stamping shapes and cuts metal sheets using dies and presses. It’s a versatile method capable of producing intricate designs with high precision.
Stamping Process
A metal sheet is placed on a die. The press then applies force to cut or shape the metal. This process can include blanking, bending, coining, and embossing.
Industrial Applications
Stamping is widespread in the automotive, electronics, and appliance industries. It provides rapid production of complex parts at a low cost.
Water Swelling
What is Water Swelling?
Water swelling, or hydroforming, uses high-pressure water to shape metal. This method creates strong, lightweight components with complex shapes.
Hydroforming Process
A metal tube or sheet is placed inside a die. High-pressure water is then injected, causing the metal to conform to the die shape. This method ensures uniform thickness and strength.
Benefits and Uses
Hydroforming is used in automotive and aerospace industries to create lightweight, durable parts. It reduces the need for welding and secondary operations.
Forging
Basics of Forging
Forging shapes metal using compressive forces. This process increases the strength of the metal by aligning its grain structure.
Forging Techniques
There are several forging methods: open-die, closed-die, and ring rolling. Each technique offers different advantages in terms of shape complexity and production volume.
Applications
Forging is essential in producing high-strength components for aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. It’s valued for its ability to produce parts with superior mechanical properties.
Cold Forming
What is Cold Forming?
Cold forming shapes metal at room temperature. This method uses high pressure to deform the metal, enhancing its strength and hardness.
Cold Forming Process
Metal is fed into a die. A punch then exerts force to shape the metal. This process can include extruding, heading, and upsetting.
Advantages and Applications
Cold forming is used in manufacturing fasteners, bearings, and fittings. It offers excellent material utilization and produces parts with superior surface finish.
Hot Forming
Introduction to Hot Forming
Hot forming shapes metal at elevated temperatures. This method allows for greater deformation and reduces the risk of cracking.
Hot Forming Process
Metal is heated to a specific temperature, then deformed using a die. The high temperature makes the metal more ductile, facilitating complex shapes.
Industrial Uses
Hot forming is used in producing automotive components, aerospace parts, and structural elements. It allows for the creation of intricate designs with high strength.
Product Quality Inspection
Importance of Quality Inspection
Quality inspection ensures that formed metal parts meet specified standards. It involves checking dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties.
Inspection Methods
Various techniques are used, including visual inspection, dimensional measurement, and non-destructive testing. Each method ensures that parts are free from defects and meet performance requirements.
Role in Manufacturing
At Altron’s, quality inspection is integral to our manufacturing process. It ensures that every part meets our high standards and satisfies customer expectations.
Conclusion
Metal forming is a critical process in manufacturing, enabling the production of high-quality components across various industries. At Altron’s, we utilize advanced metal forming techniques to deliver precision-engineered parts that meet the highest standards. From metal spinning to hot forming, our methods ensure reliability, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Through rigorous quality inspection, we maintain excellence in every product we produce.
ALTRON‘s Metal Spinnning Froming Services:
WhatsApp: +86 156 2739 7226
E-mail: info@auto-altron.com

Hot Metal Spinning Process

Centrifugal fan impeller internal welding robot

Lampshade metal polishing process
Metal spinning products 3D laser cutting
